Home » What is Smoke Testing in Software Development?
Jinn
Content Writer · 8 min read · Aug 11, 2025
Smoke testing is a crucial yet often overlooked step in software development. It helps ensure build stability and prevents wasted time on broken deployments. This article explains what smoke testing is, when to use it, and includes practical examples
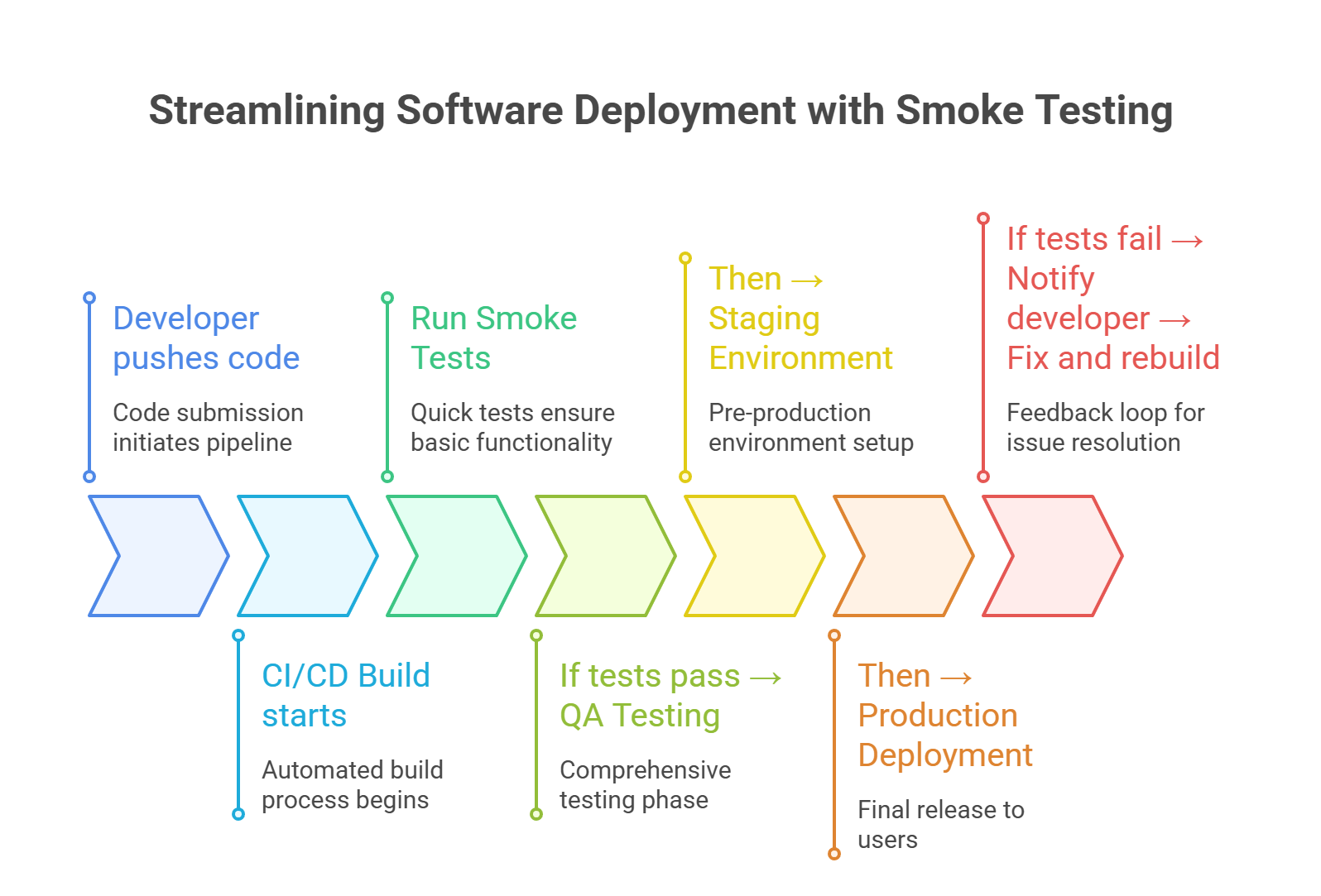
Smoke testing is a high-level type of software testing conducted to determine whether the most important functions of an application are working properly. It’s often called a “build verification test”, as it ensures that the build is stable enough for further, more detailed testing
The name is an analogy borrowed from hardware testing: “When you turn on a new piece of hardware for the first time, you watch for smoke. If you see smoke, you know something is seriously wrong and you don’t need to proceed with more detailed testing.”
If the smoke test fails – testing stops until the build is fixed
The primary functions of quality assurance include:
Smoke testing is typically done at the initial stages of testing, right after a new build is deployed. Common scenarios include:

Here are some real-world examples:
Web Application Example
Feature | Smoke Test Check |
Login | Can you successfully log in with valid credentials? |
Dashboard | Does the main dashboard load without errors? |
Navigation | Do key links/routes work (e.g., Home, Settings)? |
API | Are major endpoints responding with 200 OK? |
UI | Are critical components rendering (e.g., buttons, modals)? |
SaaS Platform Example
If your team pushes a new build to QA:
If any of these fail – deeper testing is postponed
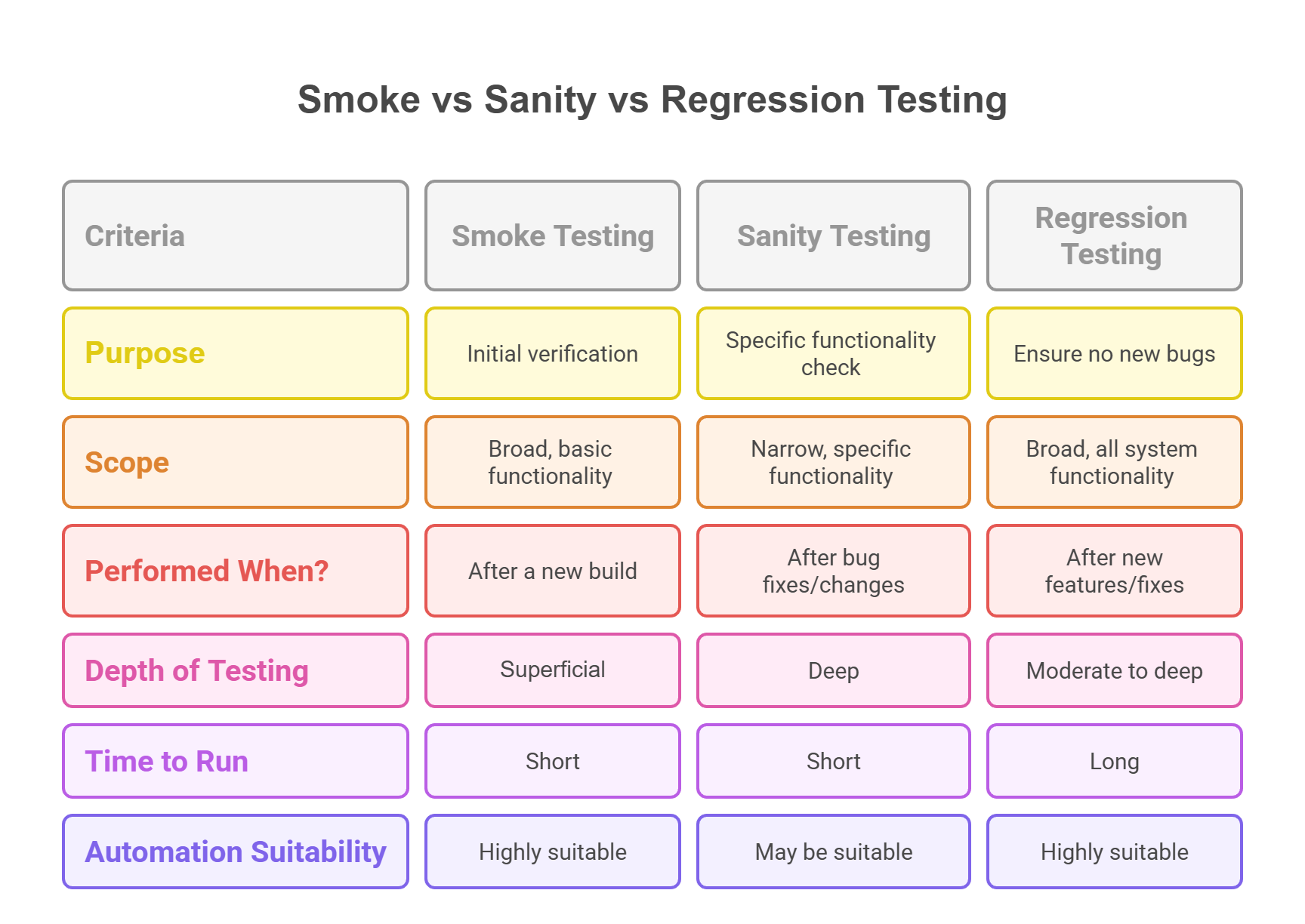
Manual vs Automated Smoke Testing
Type | Description | Use Case |
Manual | Tester executes key flows by hand | Small teams, early-stage projects |
Automated | Scripts run via CI pipelines | Mature projects, frequent releases |
Tools like Jinn Jenkins, GitHub Actions, CircleCI, and GitLab CI can automate smoke test suites to run on every commit or deployment
Smoke testing saves time and prevents headaches. By catching obvious issues early, teams avoid the trap of wasting hours on debugging a broken build or running full regression suites on an unstable application
It’s a small investment with big ROI – especially in modern CI/CD pipelines where speed and quality must go hand-in-hand
Features:
Automatic bug capture with screenshots, screen recordings, console logs, and DOM snapshots.
One-click bug reports enriched with technical context (steps, environment, system info).
Instant collaboration with in-app comments, chat, and voting on issues.
Integrates with Jira, Trello, Asana, Slack, Sentry, and more.
“Rewind” mode to replay what happened before a bug appeared.
Best For: QA teams and product squads that want to spot bugs instantly during smoke testing, share context without manual effort, and fix issues faster
Features:
Real-time dashboards for instant test results and bug tracking
Integrates with GitHub, Jira, and Slack for seamless bug reporting
Supports both manual and automated smoke tests, with one-click reruns for failed cases
Best For: Teams needing fast feedback and CI/CD integration 7
Features:
Cloud-based testing on real devices and browsers
Captures screenshots, videos, and logs automatically when tests fail
Integrates with Jira, GitHub, and Slack for bug tracking
Best For: Cross-browser and cross-device smoke testing with detailed bug evidence
Features:
Highly customizable bug tracking templates and workflows
Integrates with smoke testing tools like Testomat.io, Zephyr, and Xray
Provides real-time collaboration and detailed issue histories
Best For: Teams already using Atlassian products for end-to-end traceability
Features:
Tight integration with GitHub repositories and CI/CD pipelines
Supports labels, milestones, and automated issue creation from test failures
Collaborative environment for developers and testers
Best For: Development teams using GitHub for version control
Smoke testing is not about finding every bug, but about ensuring basic application health. It’s the first line of defense in your QA strategy and plays a vital role in maintaining rapid, safe development cycles
If you’re not running smoke tests on every build – it’s time to start
Your Personal Debugging Djinn
Smoke testing verifies that the most important and basic features of an application work after a new build. Its goal is to catch critical issues early so the team doesn’t waste time on deeper testing of a broken build
No, and this is a common point of confusion. While both are quick checks, their scope and purpose differ:
The action is straightforward: Stop further testing. The build should be rejected and sent back to the development team to fix the critical issues. Investing time in detailed testing on a broken build is a waste of resources
Both work. Manual smoke tests are fine for small teams and early projects. Automated smoke tests are best for frequent releases and CI/CD pipelines, as they give fast, repeatable feedback
If you want minimal effort and maximum visibility, Jinn is a great choice — it automatically records screenshots, videos, console logs, and DOM snapshots when something goes wrong, and turns them into ready-to-share bug reports. Other tools like Testomat, BrowserStack, Jira, and GitHub Issues are also useful, but they often require extra setup or don’t capture as much context out of the box
Yes. Even a short checklist of smoke tests saves hours by preventing broken builds from reaching QA or production. With tools like Jinn, small teams can capture bugs effortlessly, and share them with developers in one click.
Save Time, Boost Productivity
Share
Get Early Access to Jinn
Sign up now to join our waitlist and enjoy free early access as soon as we launch.
Sign up today and be a part of the future of QA.
With Djinn, bugs are understood instantly, and fixes come faster
Product
Company
Policies
Support
© 2025 All Rights Reserved
Get Early Access to Djinn
Sign up now to join our waitlist and enjoy free early access as soon as we launch.
Sign up today and be a part of the future of QA.